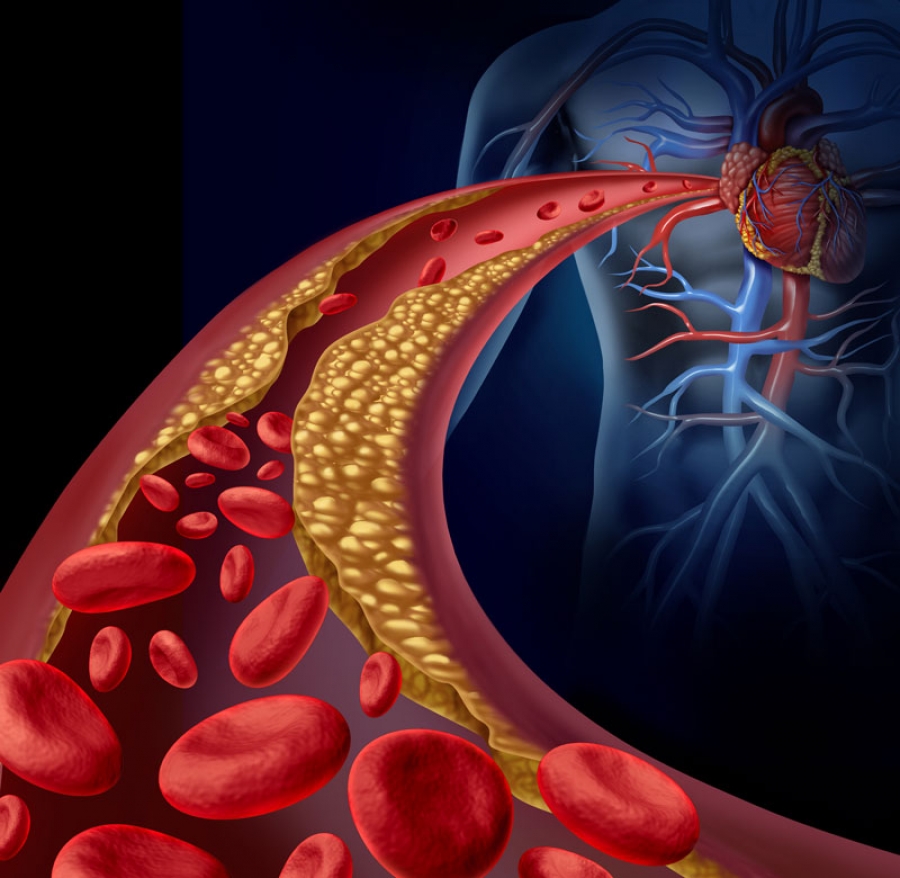
Atherosclerosis can lead to serious problems, including:
- Coronary artery disease. These arteries supply blood to your heart. When they are blocked, you can suffer angina or a heart attack.
- Carotid artery disease. These arteries supply blood to your brain. When they are blocked you can suffer a stroke.
- Peripheral arterial disease. These arteries are in your arms, legs and pelvis. When they are blocked, you can suffer from numbness, pain and sometimes infections.
Symptoms
The symptoms of the disease depend on which arteries are affected:
- Carotid Arteries
Carotid arteries provide blood to the brain, when the blood supply is limited patients can suffer stroke and may experience:- Weakness
- Difficulty breathing
- Headache
- Facial numbness
- Paralysis
- Coronary Arteries
Coronary arteries provide blood to the heart, when the blood supply to the heart is limited it can cause angina and heart attack, symptoms include:- Vomiting
- Extreme anxiety
- Chest pain
- Coughing
- Feeling faint
- Renal Arteries
Renal arteries supply blood to the kidneys; if the blood supply becomes limited, there is a serious risk of developing chronic kidney disease, and the patient may experience:- Loss of appetite
- Swelling of the hands and feet
- Difficulty concentrating
- Peripheral arterial disease
The arteries to the limbs, usually the legs, are blocked. The most common symptom is leg pain, either in one or both legs, usually in the calves, thighs or hips. The pain may be described as one of heaviness, cramp, or dullness in the leg muscles. Other symptoms may include:- Hair loss on legs or feet
- Male impotence (erectile dysfunction)
- Numbness in the legs
- The color of the skin on the legs change
- The toenails get thicker
- Weakness in the legs
Risk Factors
- High Blood Pressure
- High levels of cholesterol
- Smoking
- High levels of sugar in the blood
- Diabetes
- Genetics – people with a parent or sibling who has had atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease are at a much higher risk
Complications
Atherosclerosis can lead to many health complications, including:
- Coronary artery disease.
- Carotid artery disease.
- Peripheral arterial disease.
- Heart Attack
- Stroke
- Kidney Disease
Being proactive and living a healthy lifestyle can help prevent or delay atherosclerosis and its related diseases. Your risk for atherosclerosis increases with the number of risk factors you have.
Living a healthy lifestyle includes:
- Heart-healthy eating - adopt healthy eating habits, which include eating different fruits and vegetables, beans and peas, whole grains, lean meats, poultry without skin, seafood, and fat-free or low-fat milk and dairy products. A heart-healthy diet is low in sodium, added sugar, solid fats, and refined grains.
- Increase your activity level - Be as physically active as you can. You need at least five days a week of moderate aerobic exercise.
- Quit smoking - If you smoke, quit. Smoking can damage and tighten blood vessels and raise your risk for atherosclerosis. Click here to read how smoking affects your health.
- Lose weight – If you’re overweight or obese, you are at higher risk for atherosclerosis. Work with your doctor on a weight loss plan.
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, your doctor may prescribe medicines to control your atherosclerosis risk factors. Take all of your medicines as your doctor advises.

Acclaimed Heart and Vascular Center
We deliver excellent care with compassion after discussing your health and treatment plan with simplicity.
DISCLAIMER: THIS WEBSITE DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE
The information, including but not limited to, text, graphics, images and other material contained on this website are for informational purposes only. The purpose of this website is to promote broad consumer understanding and knowledge of various health topics. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health care provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.